What Do They Put on Baby Eyes When They First Born
What is the history of using erythromycin eye ointment for newborns?
The use of erythromycin eye ointment in newborns has its roots in the late 1800s. Back then, near 10% of newborns born in hospitals across Europe developed an disease called ophthalmia neonatorum. This illness caused incomprehension in 3% of affected infants (Schaller & Klauss, 2001).
Ophthalmia neonatorum (ON), besides known every bit neonatal conjunctivitis, is an infection that causes inflammation of the conjunctiva during the first iv weeks of life. The conjunctiva is a layer of thin tissue that covers the inner role of the eyelid and the white part of the middle. During the late 1800s, before antibiotics were discovered, 0.3% of infants (three out of i,000) were blinded from ON (Schaller & Klauss, 2001).
Doctors had suspected since the early on 1800s that newborns caught ON after beingness exposed to something in the birth canal, but for many years nobody knew what the infants defenseless or how to prevent it. In 1879, a German physician named Albert Neisser discovered that gonorrhea—a sexually transmitted infection – was causing the ON (Dunn, 2000). The following year, another High german physician, Carl Credé, introduced a breakthrough treatment to forestall ON. Instead of waiting for signs of infection to treat with silverish nitrate solution, as doctors had been doing with footling success since the 1830s, he realized that ON could exist prevented by putting silver nitrate into the eyes of all newborns at birth. This new practice aimed at prevention was a great success. The number of ON infections in Dr. Credé'due south hospital went from 30-35 cases per year to but one case in the first six months that he started using silverish nitrate (Schaller & Klauss, 2001).
Today, more than than 130 years later on Dr. Credé made his discovery, quite a few things take changed. Showtime, antibiotics take made it possible to care for pregnant people who take sexually transmitted infections also equally any infants who contract bacterial ON—making blindness highly unlikely in countries where mothers have access to screening and handling during pregnancy. Also today, gonorrhea has been replaced by chlamydia—another sexually transmitted infection—equally the leading cause of ON, both globally and in the U.S. (Zloto et al., 2016; AAP, 2018). Another modify is that silver nitrate is no longer used because information technology is extremely irritating to the eye and tin can cause severe pain, chemical pink eye (middle irritation), and temporary vision bug (Standler, 2006). Silver nitrate is no longer available in the U.S. (neither is tetracycline eye ointment, some other antibiotic that was used in the by to prevent ON). Instead, virtually newborns in the U.S. volition have 0.v% erythromycin eye ointment put in their eyes at nativity in hopes of preventing ON.
What causes ophthalmia neonatorum (ON)?
Conjunctivitis is also normally chosen pink center due to the redness and swelling that tin can come with the infection. Pink heart tin can be caused by viruses (e.g., herpes), bacteria, chemicals, and blocked tear ducts. Every bit we have stated, today the virtually common cause of ON is chlamydia–a sexually transmitted infection responsible for ii% to 40% of reported cases of ON in the U.Due south. The sexually transmitted disease gonorrhea now accounts for less than 1% of cases.
Amongst U.S. women, chlamydial infection is nigh half dozen times more common than gonorrheal infection. In 2015, the rate of chlamydia was 646 per 100,000 females in the U.South., and the rate of gonorrhea was 107 cases per 100,000 females in the U.South. (CDC, 2015). Although chlamydia is the most common cause of ON, gonorrhea results in the most serious type of ON.
Other types of bacteria that come up from the female parent, hospital, or home environment are idea to crusade 30% to 50% of cases, and the canker virus causes less than i% (AAP, 2015).
This article focuses on ON from gonorrhea and chlamydia, since that has always been the emphasis in public health prevention. The other bacteria that crusade ON were never the targets of center ointment prophylaxis ("pro- fuh- LAX-is"). Prophylaxis means taking activeness ahead of fourth dimension to try and prevent something bad from happening. Withal, some care providers claim that the erythromycin eye ointment also offers protection from infection with bacteria like staph and strep. We will talk over the evidence for this practise after in the article.
The only way for a newborn to contract ON from chlamydia or gonorrhea is if the mother has an untreated infection at the time of giving nascency. Of newborns born to mothers with untreated gonorrhea, betwixt 1 in 2 to 1 in three of them risk developing gonorrheal ON, which carries with it a high take chances of incomprehension. Left untreated, gonorrheal ON can brainstorm to cause vision loss in as little every bit 24 hours. The risk of a newborn getting chlamydia from an infected mother ranges from 8% to 44%, with the best estimate around 15%. Chlamydia has a low run a risk of blindness but can even so cause centre damage and, rarely, loss of vision if non treated (Kapoor et al., 2016).
In sub-Saharan Africa, ON remains a major crusade of blindness, generally due to untreated gonorrheal ON (Whitcher et al. 2001). Serious complications from ON are rare in the U.S. and other countries with high rates of prenatal screening and treatment for sexually transmitted infections and quick access to oral or injectable antibiotics should ON develop. In fact, we could not find whatsoever published reports of blindness in newborns with ON who had been treated with antibiotics subsequently getting an infection. Antibiotics are highly effective at treating bacterial ON and eye damage tin can be avoided if antibiotics are given promptly after an babe develops ON (Darling & McDonald, 2010).
Can a baby become ON after a Cesarean?
If a baby is built-in past Cesarean then it is extremely unlikely that the baby could develop ON, particularly if the mother'south water never bankrupt before surgery (Medves, 2002). Notwithstanding, the current recommendation of the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) is that in regions with loftier rates of gonorrhea and when prenatal care is not accessible, erythromycin should be put into the eyes of all newborns to prevent gonorrheal ON, including infants born past Cesarean, since ascending infection can occur (AAP, 2018).
By ascending infection, the AAP means that gonorrhea and chlamydia are physically able to infect the fetus even before the fetus passes through the birth canal. Nosotros found four cases of gonorrheal ON after Cesarean (Thompson et al. 1974; Strand & Arango, 1979; Diener, 1981; Jacobsen et al. 1991). In all four cases, the mother's water had been broken for 18 to 24 hours or more earlier the surgery. Other rare case reports provide evidence that gonorrhea can infect the placenta even before the mother'due south h2o has broken and cause an infection of the membranes called chorioamnionitis, and sepsis (Yvert et al. 1985; Smith et al. 1989). Chlamydial ON has as well occurred afterwards Cesarean in at to the lowest degree 26 babies (Givner et al. 1981; Sato et al. 1990; Yescas-Buendía et al. 1993; Wu et al. 2003; Amini et al. 2008) and at least ane of these transmissions is thought to have occurred even though the mother'south water had not cleaved at the time of surgery (Shariat et al. 1992).
So, in summary, information technology is possible for a newborn to get gonorrheal or chlamydial ON later on a Cesarean, just the bodily risk is unknown because it's so rare.
Which is a better strategy: Worrying almost sexually transmitted infections during pregnancy or afterward nascency?
Untreated gonorrheal and chlamydial infections during pregnancy take been associated with many other complications. Gonorrhea has been linked to miscarriages, stillbirths, premature birth, low birth weight, premature rupture of membranes, chorioamnionitis, and bloodstream infections. Chlamydia has been linked to preterm labor, premature rupture of membranes, depression nativity weight, and newborn lung infections (CDC, 2016).
The fact that gonorrhea and chlamydia tin can cause impairment long earlier nativity ways that it is far better to catch an infection early in pregnancy rather than to merely wait until after the birth to worry about the consequences of these infections. An ON prevention strategy that emphasizes screening, treatment, and counseling in pregnant people could assistance to decrease the risk of pregnancy-related complications, every bit well as newborn ON.
How practise y'all know if a mother is at risk for chlamydia or gonorrhea?
Anyone who is sexually active can go chlamydia or gonorrhea through vaginal, anal, or oral sex. A male person partner does not have to ejaculate in order to give the infection to his partner. Re-infection is possible after a previous treated infection. Nigh people have either no symptoms or balmy symptoms (CDC, 2016).
You tin avoid both chlamydia and gonorrhea if you are in a monogamous relationship in which both partners have been tested and are uninfected. If that is not your state of affairs, then you lot can reduce your risk by using latex condoms the right way every time you lot take sex. Your risk of getting chlamydia or gonorrhea is higher if you are immature (under the historic period of 25), if you lot accept multiple sexual partners, if your partner has other sexual partners, or if you live in an area where in that location are high rates of infection. Washington, D.C. has the highest rates of gonorrheal and chlamydial infection in the U.S.; it reports 416 cases of gonorrhea and one,198 cases of chlamydia per 100,000 people (CDC, 2015). Exterior of D.C., the southeastern states written report the highest rates of these infections. Some countries take rates that are higher than those in the U.Due south. and some countries have rates that are lower
Why is erythromycin eye ointment used to forbid ON in newborns?
Care providers in some countries endeavour to prevent ON by giving all newborns centre ointment (such as erythromycin). The eye ointment is intended to kill or weaken leaner in the eye–particularly gonorrhea–to protect the infant from getting pink eye, since pink eye from gonorrhea can cause serious eye harm and blindness if left untreated.
Automated prophylaxis with erythromycin centre ointment for all newborns within 24 hours of nascence is currently recommended past the U.Due south. Preventive Services Task Force (2019) and their recommendation is promoted by the American Association of Family unit Physicians. However, the American Academy of Pediatrics recently called for reevaluating state mandates for erythromycin eye ointment (AAP, 2018). Instead, they propose a strategy of (1) prenatal screening for and treatment of gonorrhea and chlamydia, (2) testing unscreened people at the time of birth and treating equally needed, (3) counseling parents to bring newborns with pink heart to immediate medical attention, and (4) continuing mandatory reporting of all cases of gonorrheal ON. The AAP recommends that routine erythromycin heart ointment is still advisable in regions with high rates of gonorrhea and where prenatal screening and treatment is not widely accessible. Similarly, the Canadian Pediatric Social club recently recommended that routine, required prophylaxis with erythromycin be stopped (Moore and MacDonald, 2015).
As you can meet in the table beneath, some countries utilise ON prophylaxis, while others take stopped this practice:

State police in most U.S. states requires newborn eye prophylaxis. In 2006, a search of state police force databases institute that at least 32 U.South. states had laws requiring newborn prophylaxis against ON (Standler, 2006). In these states, health care providers are required to give the erythromycin eye ointment to every newborn, regardless of the female parent's status for chlamydial or gonorrheal infection, and regardless of whether or not the baby was built-in vaginally or by Cesarean. Some states, such as New York, practise not allow parents to practice their right to informed refusal. However, other states, such as Tennessee, have recently made changes to their state laws to allow parents to decline the erythromycin eye ointment for their infants.
What is the evidence for erythromycin prophylaxis to forestall newborn pink middle?
In 2010, researchers combined results from viii studies (chosen a meta-assay) that looked at the effectiveness of various middle ointments to prevent ON (Darling & McDonald, 2010). The use of erythromycin was examined in four of those studies, including a total of four,514 participants. As you lot can see from the table below, erythromycin was more than effective than silverish nitrate at preventing chlamydial ON – the researchers found a 29% decrease in the risk of chlamydial ON among the infants who received erythromycin compared to silver nitrate. They did not discover whatever evidence that erythromycin is better than silver nitrate at preventing gonorrheal ON. However, finding no difference between the 2 types of prophylaxis does non mean that erythromycin was non effective. Researchers may consider it unethical to give no prophylaxis to infants in geographic areas with high rates of gonorrheal and chlamydial ON, then erythromycin is compared to silver nitrate instead of a no treatment group. Silverish nitrate is no longer used in many countries simply information technology's useful for comparison with erythromycin. Only one trial has ever randomly assigned babies who were potentially exposed to chlamydia and gonorrhea to receive erythromycin or no prophylaxis. The study of 4,544 newborns in China plant that neither erythromycin, silver nitrate, nor tetracycline reduced the gamble of chlamydial ON compared to no prophylaxis at all (Chen, 1992).
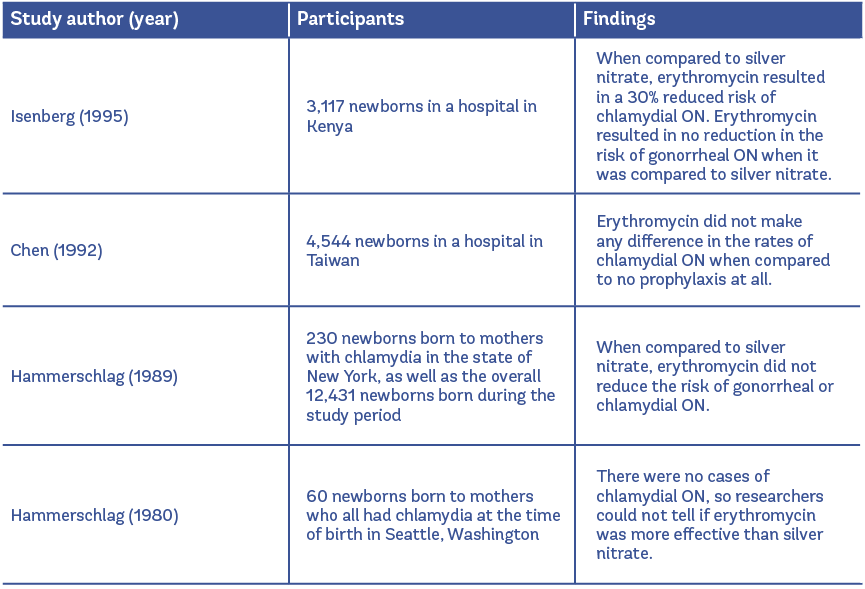
The overall quality of these trials was depression (the Darling & McDonald reviewers agreed that all had at to the lowest degree i expanse of major weakness), and so it is necessary to look at other types of studies to determine the effects of ON prophylaxis. A few studies have treated newborns with prophylaxis and compared their rates of gonorrheal or chlamydial ON to infants in the by who did non receive any prophylaxis. In a large observational report in Southward Africa, no heart prophylaxis was used for a certain amount of time, and then iii hospitals started using argent nitrate and erythromycin. When they compared no prophylaxis to prophylaxis amidst thirty,530 newborns, the number of gonorrheal ON infections dropped from 273 cases per 100,000 births to 34 cases per 100,000 births. Yet, within the prophylaxis group, there was a failure rate of 20%, in which the eye ointment did not work to foreclose ON (Lund et al. 1987).
Hammerschlag et al. conducted a trial that included 230 infants born in Brooklyn, New York, to mothers with known chlamydial infections. They found that the rates of chlamydial ON were lower in the groups who had prophylaxis compared to newborns in the by whose mothers had chlamydia and did not receive any prophylaxis (eleven-xx% tdsus 33%) (Hammerschlag et al. 1989). Laga et al. also conducted a trial and found that chlamydial ON was reduced by 68% to 77% in the infants given prophylaxis compared to infants from the past who did not receive whatever prophylaxis (Laga et al. 1988).
The authors of the Darling & McDonald meta-analysis looked over these studies and concluded that, overall, rubber eye ointments may help to prevent chlamydial ON, but not likewise as they assist to prevent gonorrheal ON. Erythromycin was more constructive than silver nitrate at preventing chlamydial ON, so that means it may offering some amount of protection. However, the evidence is then questionable that erythromycin (or whatever other prophylactic eye ointment) offers whatsoever amount of protection confronting chlamydial ON that groups similar the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Canadian Pediatric Society take concluded that rubber eye ointments cannot forbid chlamydial ON (AAP, 2018; CPS, 2015).
As far as treatment goes after infants develop an infection, eye ointment is non effective for treating gonorrheal or chlamydial ON. Both require oral or 4 antibiotics. To treat gonorrheal ON, most infants need 1 dose of ceftriaxone (25-50 mg/kg, intravenously or intramuscularly, not to exceed 125 mg, depending on the care provider'due south assessment). To treat chlamydial ON, most infants should receive oral erythromycin or ethylsuccinate (50 mg/kg/day in 4 divided doses daily) for 14 days or azithromycin (twenty mg/kg as a single daily dose) for three days (AAP, 2018).
Does erythromycin preclude ON from other bacteria, such equally staph?
The following leaner are idea to crusade 30-50% of ON infections:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae, nontypeable
- Group A and B streptococci
- Corynebacterium species
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Escherichia coli
- Klebsiella pneumoniae (AAP, 2018)
These leaner live on the skin and in the lungs, vagina, stomach, and intestines. They are picked up during birth or from hospital or abode exposures after the birth. Health care workers and other people who handle newborns tin can accept the above bacteria on their bodies and not have whatsoever symptoms. This means that every fourth dimension a new person has contact with a infant, the newborn's chance of exposure increases (Sherertz et al. 2001).
Newborn pinkish eye caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria is at least as common as pinkish heart from gonorrhea, and information technology can exist only as severe (AAP, 2018). Infection can progress rapidly to eye damage, blindness, serious systemic infection, and death. The leaner can alive on health intendance workers' bodies and in the environment, peculiarly in moist areas such equally plumbing for sinks and baths, feeding bottles, and breathing equipment (Jefferies et al., 2012). It more often than not causes infection among infants in intensive care units. We didn't find whatsoever evidence that routine eye ointment helps to prevent pseudomonal ophthalmia. Of business organization, xiii% of strains take been establish to be resistant to nearly all or all antibiotics. For this reason, the CDC considers multi-drug resistant pseudomonas infections to be a serious threat (CDC, 2013)
Other than Pseudomonas aeruginosa, most non-gonorrheal and non-chlamydial leaner in the newborn'southward eyes are non dangerous and practise not progress to blindness. Nevertheless, these bacteria have been found in the eyes of newborns with pinkish heart (Bramantyo, et al. 2015). Whether or non they caused the pinkish heart is less well understood. Bacteria similar Staphylococcus aureus, for example, are ofttimes plant in the eyes of newborns who do not accept pink heart (Kapoor et al., 2016).
Erythromycin eye ointment is a ordinarily prescribed handling for non-gonorrheal, non-chlamydial conjunctivitis (Bremond-Gignac et al., 2011). Even so, inquiry has shown that erythromycin can prevent gonorrheal ON, and possibly chlamydial ON to some extent (although it is controversial), just at that place is little evidence that this is an effective prevention strategy for ON from other bacteria.
We did find a few studies that have looked at whether middle ointment can reduce the number of overall bacteria in the newborn's optics, similar to how information technology reduces leaner in petri dishes in a laboratory setting (Ibhanesebhor & Otobo, 1996).
One report measured the number of bacteria in newborn optics after treatment with iii types of eye ointments (Isenberg et al. 1995). In this study, newborns in Kenya were randomly assigned to three groups: povidone-iodine (1,076 newborns), erythromycin (ane,112 newborns), or silver nitrate (929 newborns). Povidone-iodine is a disinfectant drop that can be placed into the newborn'south eyes. The center prophylaxis given inside twenty minutes of the birth. Infants who returned to the hospital with pink heart were swabbed and the results were studied at the laboratory. If no organism could be found, then the infant was considered to have non-infectious, or chemic, pink center.
After the utilize of prophylaxis, infectious ON still occurred in 13%, xv%, and 18% percentage of newborns treated with povidone–iodine, erythromycin, and argent nitrate, respectively. The most commonly found bacteria among the infants with pink eye was chlamydia (50%), followed by Staphylococcus aureus (xl%). Compared to the grouping that received povidone-iodine, groups that received silver nitrate and erythromycin had overall rates of pink eye that were 34% and 16% higher, respectively. All three types of prophylaxis reduced the number of bacteria in the eyes of the newborns compared to the amount of bacteria typically found in newborn eyes before prophylaxis (Personal correspondence, Isenberg, 2017).
A study in Islamic republic of pakistan compared 2.v% povidone-iodine solution and 1.25% povidone-iodine solution in 100 healthy infants (Khan et al. 2016). A swab for bacterial culture was taken thirty minutes afterwards birth. Then, a single drib of two.five% concentration was put in the right eye and 1.25% concentration was put in the left eye. They found that both drops reduced the number of leaner, and that the 1.25% concentration was as effective every bit the 2.5%. Similarly, a trial in Republic of indonesia compared ii.5% povidone-iodine solution to 1% Chloramphenicol antibiotic ointment in sixty healthy newborns (Bramantyo et al. 2015). They found that both types of prophylaxis were equally effective at reducing the bacteria.
In 2014, researchers in Iran randomly assigned 300 newborns to ane of 3 groups: two drops of colostrum (the female parent's first breast milk afterward the birth), erythromycin, or nix (Ghaemi et al. 2014). To be included in the trial, the newborns had to accept no bacteria in their optics immediately after the birth. After receiving the prophylaxis (or none, in the group assigned to nothing), the infants were watched to meet if they developed pink eye in the first 28 days after birth. All of the infants who adult pinkish center were swabbed and found to have Staphylococcus aureus. ON was most mutual in the infants that did not receive whatsoever prophylactic treatment (33%), followed by the group receiving colostrum drops (24%) and the group receiving erythromycin (sixteen%). This study provides evidence that erythromycin may offer some protection confronting ON from staph bacteria.
The idea behind this strategy to give heart ointment in order to prevent ON from non-gonorrheal and non-chlamydial leaner is that by lowering the amount of overall bacteria in a newborn'south eyes, nosotros could potentially be lowering the risk of ON from bacteria such as staph and strep. One trial found that erythromycin reduced ON from staph compared to no treatment or drops of colostrum. However, the enquiry on using erythromycin to forestall ON from non-gonorrheal and non-chlamydial bacteria is very limited. Then, at this point, we don't know if this is an constructive strategy or not. As well, this strategy may exist express by antibiotic resistant leaner, which we will discuss in the next department!
Are bacteria becoming resistant to erythromycin?
Remember, not-sexually transmitted leaner like Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, and grouping A and B streptococci are thought to cause 30% to fifty% of ON infections. When care providers recommend erythromycin prophylaxis to foreclose ON from these leaner, they might not be considering that many strains of these bacteria are now resistant to the ointment they are putting in infants' optics.
Erythromycin was commencement introduced in 1953, and by 1968, strains of Streptococcus bacteria had developed resistance. Of Streptococcus bacterial samples tested at the CDC in 2010 and 2011, ten% of grouping A were erythromycin-resistant, while half (49%) of Group B Strep strains were erythromycin-resistant (CDC, 2013). Resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus have also been reported in newborns with ON who were given erythromycin prophylaxis (Hedberg et al. 1990).
Gonorrhea – the primary target of ON prevention campaigns – is also becoming resistant to erythromycin. In 2012, strains isolated in Canada showed a 23% resistance to erythromycin. Information technology is not known whether this resistance tin can be overcome by using higher levels of antibiotics. The studies that testify erythromycin to be constructive prophylaxis for gonorrheal ON are non current and may not exist as relevant today due to growing resistance (CPS, 2015).
Antibiotic resistance is rare in chlamydia, and people are not withal sick with antibody-resistant strains (Sandoz & Rockey, 2010). However, strains of chlamydia that are resistant to erythromycin have been found in a laboratory setting (Welsh et al. 1992).
Povidone-iodine is an alternative eye treatment that is thought to be effective against a wide multifariousness of bacteria without encouraging the evolution of bacterial resistance (Kapoor et al., 2016).
As a side notation, at that place is no evidence that routine erythromycin middle ointment prophylaxis is causing the increase in drug resistant strains of bacteria. The drug resistance is more likely an effect of oral antibiotics that many people are taking, rather than the one fourth dimension utilise of a topical ointment in newborns (Personal correspondence, Dr. Arbeter, 2017). However, the drug resistance is probably making the erythromycin eye ointment less effective.
It may be helpful to summarize the risks and benefits of erythromycin prophylaxis like this:
Benefits:
- Erythromycin has been shown in the past to reduce the risk of gonorrheal ON – thereby reducing the risk of incomprehension from the infection – and maybe, chlamydial ON (Darling & McDonald, 2010)
- Some evidence suggests that erythromycin reduces overall bacteria in the eye and may help to preclude ON from non-sexually transmitted bacteria like staph (Isenberg et al. 1995; Ghaemi et al. 2014)
- Erythromycin prophylaxis may be helpful if the mother and her partner(south) did not receive adequate screening and treatment for gonorrhea during the pregnancy and it'due south not possible to examination the mother at the fourth dimension of nascence and treat the babe as needed (CPS, 2015)
- Erythromycin prophylaxis may assistance to protect a newborn from gonorrheal ON if the mother was infected after a negative screening effect earlier in the pregnancy (for example, due to a partner's infidelity)
- Erythromycin prophylaxis may exist helpful in geographic areas where rates of gonorrhea are very high, especially combined with low rates of prenatal care (Medves, 2002)
- Erythromycin eye ointment is cheap (Darling & McDonald, 2010)
Risks:
- Adverse effects tin include chemical pink eye, or eye irritation. A study in Kenya found that 13% of infants who received erythromycin developed pink eye with no bear witness of infection (culture-negative) (Isenberg et al. 1995). If chemical pink eye is mistaken for bacterial pink eye, it could lead to treatment with more antibiotics while waiting for civilisation (exam) results.
- Blurred vision could potentially interfere with bonding past disrupting early eye gazing between the newborn and parents (Personal correspondence, Brazelton Institute, 2017; Bruschweiler-Stern, 2009). Although bonding is hard to written report, it'due south been shown that from nascence, newborns tin tell between direct and indirect eye contact, and that newborns adopt when they can mutually gaze with their parent (Farroni et al. 2002).
- Erythromycin is not 100% constructive at preventing gonorrheal ON – it had a 20% failure rate in the past and might be less effective now due to growing resistance (Lund et al. 1987)
- Erythromycin may not exist effective at preventing chlamydial ON or ON from other not-gonorrheal bacteria (CPS, 2015)
Are there any other options abreast the erythromycin?
Screening and treatment of sexually transmitted infections during pregnancy
One option is for the female parent to be screened for sexually transmitted infections during pregnancy and receive antibiotic treatment, along with her sexual partner(s), if needed. If the mother is treated, then she would need follow-up testing to make sure the treatment was effective. If a mother is not infected with gonorrhea and is in a monogamous relationship with an uninfected partner, then newborn centre ointment may be reasonably declined (Medves, 2002).
The benefit of this option is that a potentially harmful sexually transmitted infection can be found and treated, improving the health of both the mother and the newborn (Coutanceau et al. 2015). The disadvantage is that if this is done on a large calibration, information technology requires a well-organized maternity care organization in which all pregnant people have access to prenatal care that includes screening for sexually transmitted infections and receiving handling as needed. Although this is possible in some countries, it may not be in others. And even within countries, not all pregnant people receive the same prenatal care. In the U.Due south., the Centers for Illness Control recommends that all pregnant people under 25 years of historic period be screened for chlamydia and gonorrhea at the get-go prenatal visit, and that those over 25 at high take chances for either infection exist screened equally well (CDC, 2016)
Another disadvantage of the screen-and-treat method is that a person may test negative for chlamydia or gonorrhea early on in pregnancy, but then be infected by a partner before giving birth. According to research from the National Opinion Research Centre's Full general Social Survey, 20%-25% of married men anonymously reported to ever having cheated on their spouse. It's of import to remember that given the potential for infidelity, any sexually agile significant person could exist at chance for gonorrheal infection, and their newborn could also be at risk for gonorrheal ON. Some intendance providers may feel that information technology is a leap of faith to ask meaning people about their sexual history, if they and their partner(south) have been tested for sexually transmitted infections, and if they are in a monogamous human relationship.
The Canadian Pediatric Order recently recommended discontinuing the routine use of eye ointment prophylaxis (CPS, 2015). They propose a screening and handling strategy every bit an alternative to required prophylaxis that includes these recommendations:
- Screen all meaning people for gonorrhea and chlamydia at their starting time prenatal visit.
- Positive test results require treatment with antibiotics during pregnancy and a re-examination in the third trimester (or, declining that, at the fourth dimension of nascency with the most rapid tests available); partners should too exist treated.
- Negative test results crave repeat screening in the third trimester or at the time of nativity if the mother was at high risk of getting the infection during the pregnancy.
- If the mother tests positive for gonorrhea at the time of birth, then the newborn should be treated with injectable antibiotics without waiting for test results and should exist farther evaluated if unwell in any manner. This recommendation includes babies built-in past Cesarean.
- If the mother tests positive for chlamydia at the time of birth, then the newborn should exist closely watched for symptoms of pink center and treated merely if the infection occurs.
In response, the Canadian Association of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus express concern with the new recommendations and urge provincial/territorial committees to keep the required centre ointment (Mulholland & Gardiner, 2015). They argue that there is no evidence to show that screening is a more effective prevention strategy than eye ointment prophylaxis. They also talk over several ways that a screening-simply arroyo could neglect. For example, they mention that there could be false-positive tests, false-negative tests, lack of prenatal care or follow-up, bacterial resistance to treatment for prenatal infections, and possible medication side effects.
It's important to realize that public wellness guidelines are all-time tailored to specific populations. The CPS's recommendation is for Canadian people who receive care from a mostly single-payer health system (national health insurance). In Canada, in that location is less variation in healthcare access and use compared to a land like the U.S., where a person's ability to access healthcare varies by insurance status. A screen-and-treat strategy would be less constructive in a country with big numbers of people unable to access timely medical care (Personal correspondence, Dr. Arbeter, 2017). A plan similar to the CPS recommendation might work in the U.S., just would need to exist studied after going into effect to see if cases of ON (from gonorrhea, chlamydia, or other bacteria) increase or decrease compared to required eye ointment prophylaxis. Nevertheless, as nosotros discussed, the American Academy of Pediatrics recently shifted their position on routine erythromycin eye ointment too (AAP, 2018). They now question the ceremoniousness of legal mandates and instead advocate for states to adopt prevention strategies more than in line with the screen-and-treat approach.
Some other selection is to expect and run into if a newborn develops ON.
This wait-and-see approach is currently used in the United Kingdom, where they don't regularly screen all pregnant people for gonorrhea and chlamydia. If a newborn did not receive eye ointment and develops pinkish eye, the virtually important factor that a doc or midwife will consider is the potential for the mother to have been infected with gonorrhea or chlamydia at the time of the birth. If information technology is unlikely that the newborn was exposed to an untreated infection, so minor pink eye is common and tin be closely watched and treated as needed. However, if the pink centre develops into pus-containing discharge, and then the infant should be hospitalized immediately then that samples tin can be tested for gonorrhea. Treatment with injectable antibiotics should brainstorm while waiting for test results (Prissy, 2012).
The disadvantage of this approach is that it relies on quick access to injectable antibiotics. If parents don't seek firsthand medical care for a newborn with pus-containing pink centre – either considering they don't recognize the potential seriousness of the infection or considering they lack admission to care – and then pink eye from gonorrhea can start to crusade centre damage inside 24 hours.
Another option is Povidone-iodine
Povidone-iodine eye drops are becoming popular in some countries because they are less expensive than erythromycin. This disinfectant does not increase the hazard of antibiotic resistance and information technology is only as effective every bit erythromycin and argent nitrate at preventing gonorrheal ON. Povidone-iodone is too thought to be more effective than silver nitrate and equally effective as erythromycin at preventing chlamydial ON. Some other advantage is that the newborn's eye turns temporarily chocolate-brown afterward putting in the drops, which helps the provider know whether full coverage was achieved.
Some U.S. doctors use 5% povidone-iodine ophthalmic drops off-label for adenoviral pink eye; however, newborn eye drops made out of povidone-iodine are not notwithstanding bachelor in the U.South. Nosotros would need a 2.5% or ane.25% solution for ON prophylaxis. A recent report suggests that the lower concentration may exist merely as effective (Khan et al. 2016).
Another option is colostrum, or the first chest milk after the nativity.
Three randomized trials have looked to see if applying drops of the mother's first breast milk into the newborn'southward optics tin can help to lower the risk of ON from non-chlamydial, not-gonorrheal bacteria. All 3 trials institute that drops of the mother's first milk can lower the chance of ON from non-sexually transmitted bacteria meliorate than no condom handling. The findings disagree, however, with regard to how colostrum compares to antibiotic prophylaxis – ane trial found colostrum to be more than effective than the antibiotic and some other found it to be less.
Earlier, we mentioned a 2014 report from Iran that randomly assigned 300 newborns who were non exposed to chlamydia or gonorrhea to ane of three groups: two drops of colostrum, erythromycin, or nothing (Ghaemi et al. 2014). They constitute that ON from staph bacteria was nearly common in the infants that did not receive any prophylactic treatment (33%), followed by the group receiving colostrum drops (24%) and the group receiving erythromycin (xvi%).
An earlier trial, also in Iran, randomly assigned newborns to one of two groups: centre drops of colostrum/breast milk prior to each breast feeding for the starting time ten days of life (327 newborns) or prophylactic treatment with an antibiotic (238 newborns). (The commodity is not in English and it is non clear which antibiotic was used.) Pinkish eye occurred in nine% of the babies receiving breast milk drops and 26% of the babies receiving the antibiotic. The most common crusade of ON in both groups was Staphylococcus bacteria (Pishva et al. 1998).
In 1982, Indian researchers at a New Delhi hospital swabbed the optics of newborns within 12 hours of nascency (Singh et al. 1982). The newborns who had negative bacteria cultures were randomly assigned to a driblet of their mothers' colostrum in both eyes, iii times per day for three days in a row (51 newborns), or to zip (72 newborns). Pink eye or a more balmy condition called "sticky eyes" was observed in 35% of the infants who received no prophylactic handling versus six% of the infants who received colostrum drops. The nearly common bacteria isolated from both groups was Staphylococcus.
Other research shows that breast milk may be effective at resolving newborn pink eye acquired by a tear duct being blocked at nascency (Verd, 2007). Researchers in Spain looked at breast milk'south ability to resolve newborn pinkish eye caused past a tear duct being blocked at birth. Researchers randomly assigned 25 patients to treatment with antibiotics and 45 patients to treatment with chest milk. By the 30th twenty-four hours of life, pink eye had resolved in 15% of the infants receiving antibiotics and 57% of the infants receiving breast milk drops. By the 60th day of life, 50% of the infants receiving antibiotics and 90% of the infants receiving chest milk drops were cleared of pink middle. The treatments continued until the 150th day of life, at which point 90% of the antibiotic group was clear compared to 100% of the breast milk group.
Three other studies accept looked at breast milk's power to inhibit, or limit the growth of leaner in a laboratory setting, called "in vitro" studies. I study compared chest milk to a broad-spectrum antibiotic (polymyxin B sulfate/trimethoprim) or no treatment in the power to inhibit the growth of 9 bacteria capable of causing ON (Baynham et al. 2013). Breast milk was improve than no treatment for three of the nine bacteria: Gonorrhea, Moraxella catarrhalis and viridans group Streptococcus. Interestingly, chest milk was better than the antibiotic for one particular bacteria: gonorrhea. The antibiotic was amend than breast milk for the other 8 species of bacteria.
The second in vitro study tested colostrum's power to inhibit the growth of chlamydia (Ramsey et al. 1998). All thirteen samples of colostrum finer inhibited chlamydial growth in a dose-response way. On average, colostrum inhibited 88% of the chlamydial growth. They found that colostrum was more effective than mature chest milk and that it started to piece of work against chlamydial growth less than fifteen minutes later on application.
In the third in vitro written report, researchers in Nigeria swabbed the eyes of 22 newborns with ON (Ibhanesebhor & Otobo, 1996). They cultured the bacteria from the eye swabs and exposed information technology to colostrum, mature milk, and a variety of antibiotics that included erythromycin. Of the positive bacterial cultures, 59% detected Staphylococcus aureus and 41% detected coliform bacteria. Coliform bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, are present everywhere in the stool of warm-blooded animals. They can exist harmless or crusade ON, and their presence means that contamination with fecal material has occurred. Staphylococcus aureus was found to be 50% inhibited by colostrum and 0% by mature milk. Coliform organisms were 57% inhibited by colostrum and 28% past mature milk. Colostrum was constructive for an boilerplate of half dozen hours after application and mature milk was effective confronting coliform organisms for an boilerplate of 3 hours. By comparison, Staphylococcus aureus was 50% inhibited past erythromycin and coliform organisms were 0% inhibited by erythromycin. And so, colostrum was but every bit effective as erythromycin at inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and more than effective than erythromycin at inhibiting the growth of coliform organisms.
Source: https://evidencebasedbirth.com/is-erythromycin-eye-ointment-always-necessary-for-newborns/
Postar um comentário for "What Do They Put on Baby Eyes When They First Born"